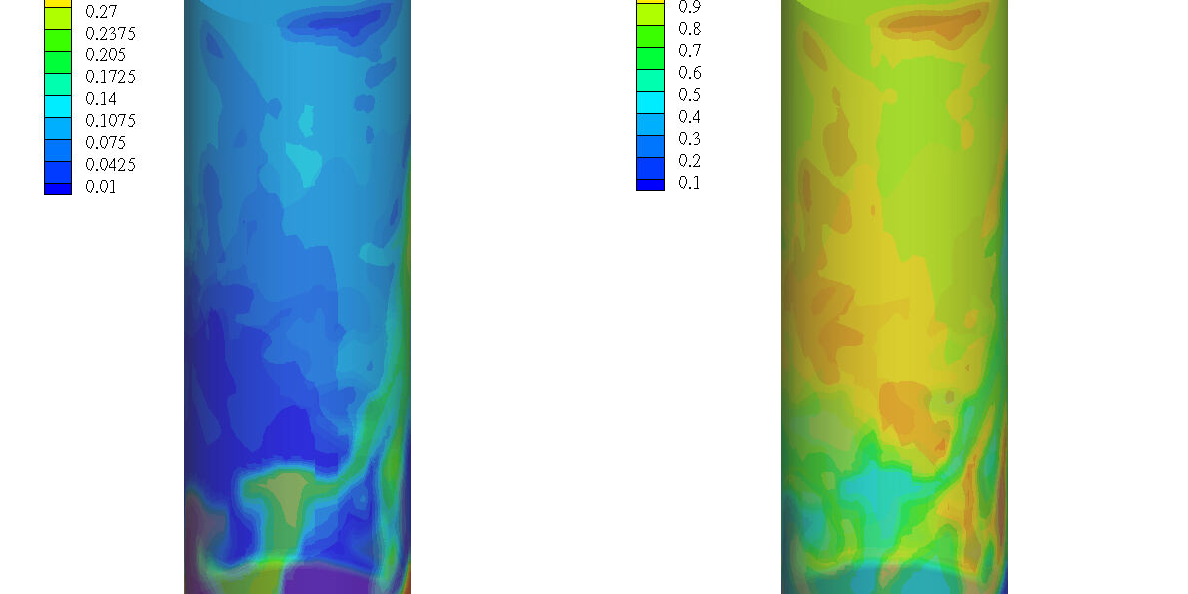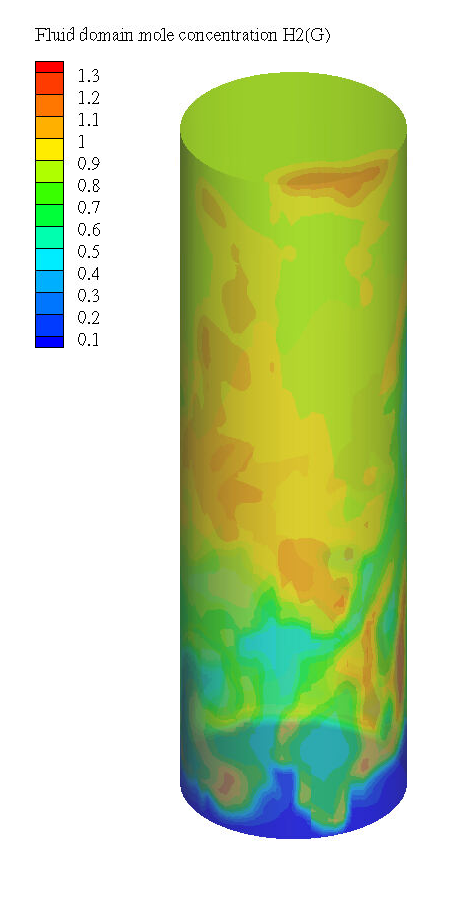
Application Model Overview
As global energy demands grow, finding sustainable alternatives to conventional energy sources is critical. Among these alternatives, bioenergy technologies like biodiesel have gained prominence for their reduced carbon emissions. However, the production of biodiesel generates an excess of glycerol, a by-product that offers the potential to produce hydrogen, a cleaner and more efficient energy source. Glycerol steam reforming (GSR) is one method under investigation for hydrogen production.
Using the Barracuda Virtual Reactor, a model was developed to simulate the GSR process. The reactor uses a nickel-based catalyst to facilitate the reaction, and a combination of steam, glycerol, and nitrogen is introduced to fluidize the catalyst bed. The goal is to produce hydrogen through the breakdown of glycerol, enabling the creation of a renewable hydrogen source.
This approach aligns with the growing need to shift from non-renewable methods of hydrogen production, such as natural gas reforming, toward more sustainable technologies. The GSR model serves as a potential pathway for industries looking to adopt greener, more efficient hydrogen production techniques.
Additional Resources
- View reaction kinetics
- Model download and instructions
- Post-processing instructions
- Xu, Jianguo and Gilbert F. Froment. “Methane steam reforming, methanation and water‐gas shift: I. Intrinsic kinetics.” Aiche Journal.
- Jin Liang, Shiliang Yang, Wengui Gao, Jianhang Hu, Hua Wang. “MP-PIC investigation of glycerol steam reforming in bubbling fluidized bed for high-quality hydrogen production”. Renewable Energy, Volume 198.
- Wang, S., Song, X., Chen, J., Wang, Q., & Lu, H. “Insights in steam reforming of glycerol in a fluidized bed by CFD modeling”. Energy & Fuels.
- M. Salomé Macedo, M.A. Soria, Luis M. Madeira. “Glycerol steam reforming for hydrogen production: Traditional versus membrane reactor”. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 44.