Application Model Overview
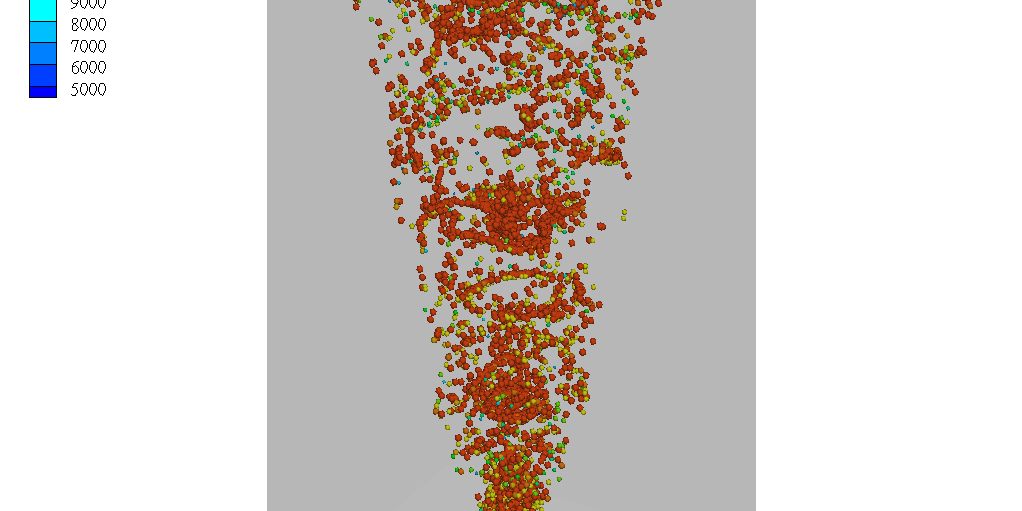
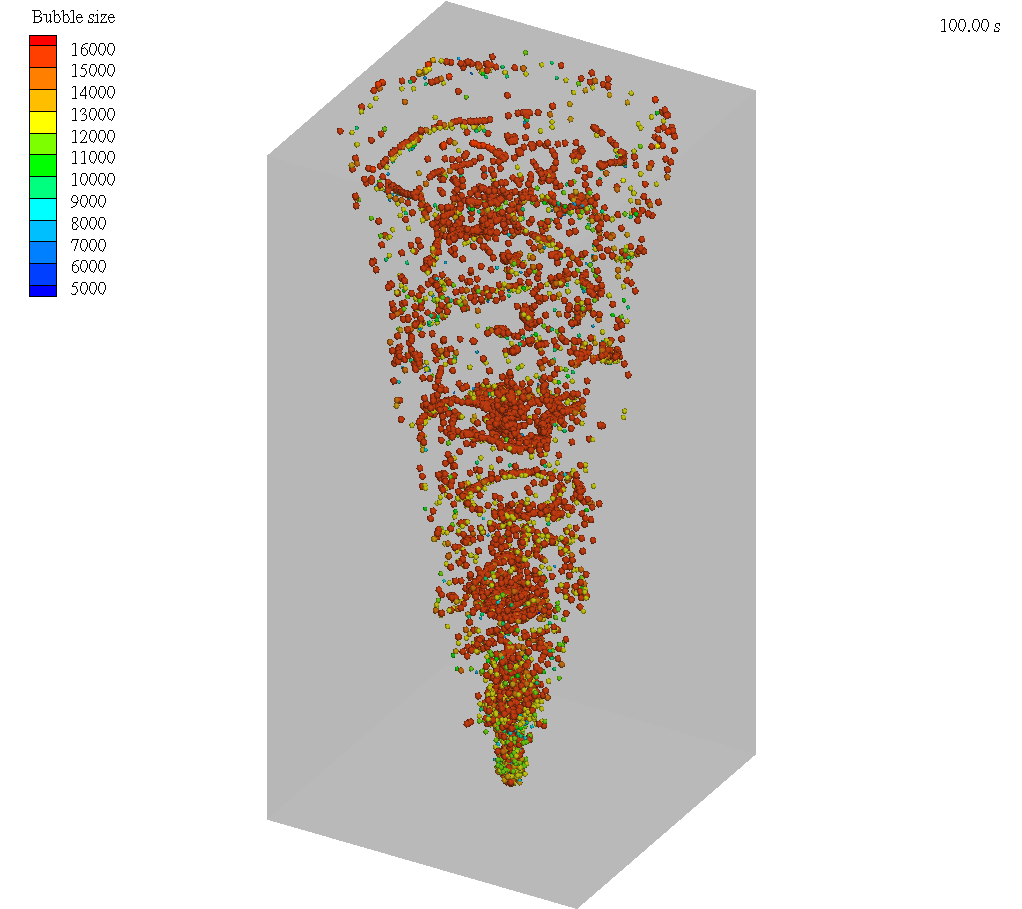
Molten metal bubble column reactors (MMBCRs) are a promising technology for clean hydrogen production and carbon capture. By injecting methane into molten metals like iron or tin, hydrogen can be produced via pyrolysis with minimal CO₂ emissions. In these systems, bubbles act as microreactors where CH₄ decomposes, and the size, shape, and motion of each bubble can significantly impact reactor efficiency.
This application model uses Barracuda Virtual Reactor to simulate argon bubbles rising through molten iron in a laboratory-scale MMBCR. While chemical reactions are excluded in this study, the simulation captures detailed bubble behavior—tracking coalescence, breakup, and diameter evolution—as a foundation for modeling more complex reactive systems.
With its ability to simulate multiphase flow involving compressible bubbles in an incompressible medium, Barracuda provides a powerful tool for analyzing bubble dynamics, supporting research and development toward scalable molten metal reactors for clean energy applications.
Additional Resources
* Support site login required. Contact us for more information on access to our customer support portal.